Vacuum Chamber use in Solar Energy Research
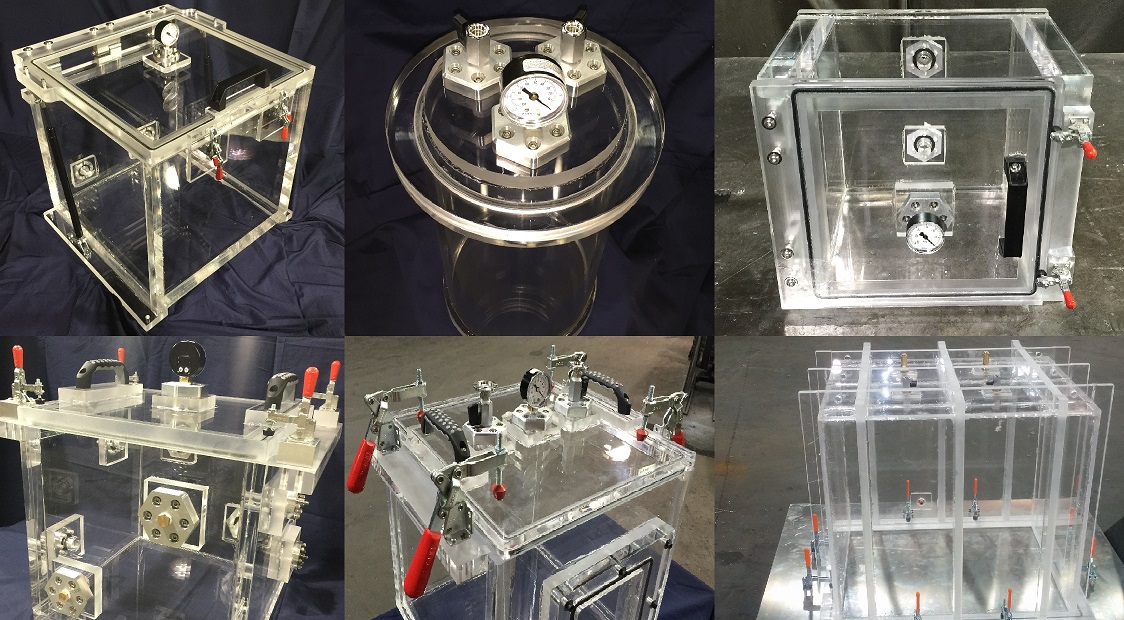
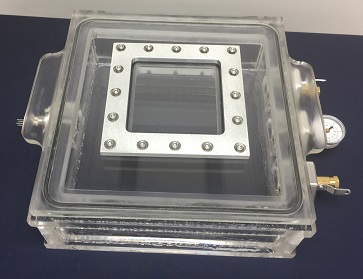
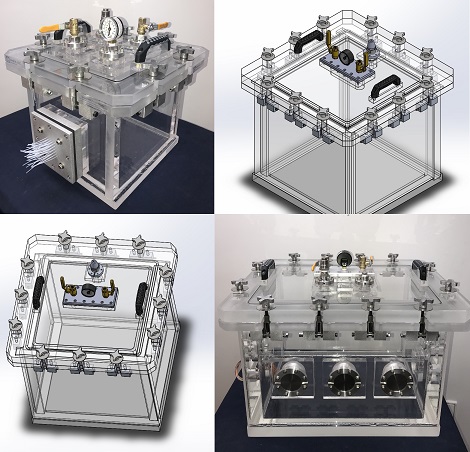
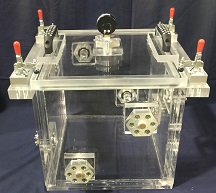
This vacuum chamber was built to perform Solar energy research on Photovoltaic Cells. We had some constrains with regards to the outside dimensions of the chamber. As you can see, it could not be too tall because it had to fit into our clients assembly jig. We therefore removed our standard lid handles and machined the handles themselves right into the acrylic chamber lid. Concurrently, we also removed our 3-Port Plate that houses the vacuum valve, the venting valve, and the vacuum gauge and moved each of them to the side wall of vacuum chamber. Finally, a way to connect electrical signals and power to the interior of the vacuum chamber from the outside, while the Solar Cell is under vacuum, was to provide an electrical feedthrough. This electrical power feedthrough was placed on the opposite wall of the vent valve, vacuum valve, and vacuum gauge.
As you can tell, there is a square and large window made from Quartz Glass coupled to the lid. The reason Quartz was used is because acrylic has limiting optical transmission properties - it does not transmit light at all in the Ultra Violet spectrum. Most of the time, this is not critical; however, in some applications, such as photovoltaics and solar power research, the transmission properties of the vacuum chamber wall become vital. Keep in mind that Ultraviolet Transmitting Acrylic does exist, but in our situation, it was not cost effective, and it did not provide replacement options.
You can read more about Ultraviolet Transmitting Acrylic Here:
Optical Transmission Properties of Acrylic
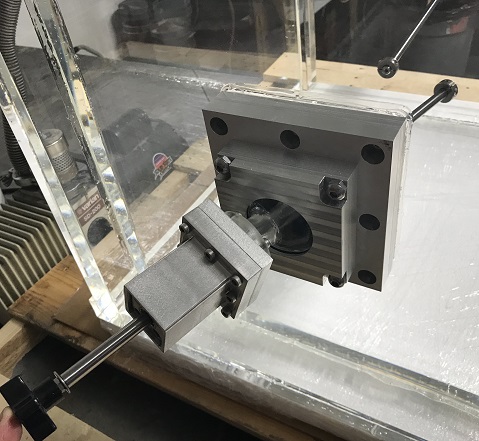
One of the advantages is also the option that our client has to remove the 6 inches by 6 inch Quartz Window and replace it with any other material with various optical transmission properties. All that needs to be done is loosen the bolts that are fastening the Window Holding Plate, made from 6061 Aluminum, remove it, remove the Glass, and replace this viewport with another Window made from a different material with different optical transmission properties such as Sapphire Glass, Borosilicate, Pyrex, etc.
We have many more resources on our website that you should check out
We make Robustly Designed and Quality Engineered Systems. What are you building? Take a look at the links below and discover some of the cool things we make.
Complete List of Articles Related to Acrylic Vacuum Chambers